Recombinant Rat Proto-oncogene c-Fos (Fos)
-
中文名稱:大鼠Fos重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP008790RA
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Fos重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP008790RA
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Fos重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP008790RA-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Fos重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP008790RA
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Fos重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP008790RA
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:FosProto-oncogene c-Fos; Cellular oncogene fos
-
種屬:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白長度:Full length protein
-
表達區域:1-380
-
氨基酸序列MMFSGFNADY EASSSRCSSA SPAGDSLSYY HSPADSFSSM GSPVNTQDFC ADLSVSSANF IPTVTAISTS PDLQWLVQPT LVSSVAPSQT RAPHPYGLPT PSTGAYARAG VVKTMSGGRA QSIGRRGKVE QLSPEEEEKR RIRRERNKMA AAKCRNRRRE LTDTLQAETD QLEDEKSALQ TEIANLLKEK EKLEFILAAH RPACKIPNDL GFPEEMSVTS LDLTGGLPEA TTPESEEAFT LPLLNDPEPK PSLEPVKNIS NMELKAEPFD DFLFPASSRP SGSETARSVP DVDLSGSFYA ADWEPLHSSS LGMGPMVTEL EPLCTPVVTC TPSCTTYTSS FVFTYPEADS FPSCAAAHRK GSSSNEPSSD SLSSPTLLAL
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Nuclear phosphoprotein which forms a tight but non-covalently linked complex with the JUN/AP-1 transcription factor. On TGF-beta activation, forms a multimeric SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex, at the AP1/SMAD-binding site to regulate TGF-beta-mediated signaling. Has a critical function in regulating the development of cells destined to form and maintain the skeleton. It is thought to have an important role in signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation. In growing cells, activates phospholipid synthesis, possibly by activating CDS1 and PI4K2A. This activity requires Tyr-dephosphorylation and association with the endoplasmic reticulum.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Fos expression in the rat olfactory neurogenic region following single exposure to maternal separation during different neonatal stages PMID: 29938674
- The hippocampal expression of Fos extra-coding RNA is required for long-term fear memory formation in rats. PMID: 27384705
- in neonatal ventral hippocampus lesion rats the expression of c-Fos was greater in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus compared to sham rats PMID: 29214513
- Study in cultured rat fibroblasts suggests that cPGES/p23 is involved in the activation of ERK to promote c-Fos expression. PMID: 29093345
- In the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), females exhibited greater c-Fos induction in response to the social interaction relative to their male counterparts, indicating a sex difference in responsivity to social stimuli. PMID: 28764933
- This study demonstrated that the c-Fos expression in auditory and visual cortices after hearing in rats. PMID: 28472857
- c-Fos-positive nuclei indicate that the rostromedial zona incerta is involved in attentional processes while adjacent tuberal lateral hypothalamus responds to arousal. PMID: 28185007
- This study demonstrated that differential stress induced c-Fos expression in the dorsal raphe and amygdala of high-responder/low-responder rats. PMID: 27865919
- UVB irradiation induced a significant reduction of the proportion of galanin positive DRG neurons for all time points, except at 12h.UVB irradiation induced increased substance P immunoreactivity in the dorsal part of the spinal cord 48h after irradiation. UVB irradiation also induced c-fos immunoreactivity in the dorsal horn and the area around the central canal 24 and 48h after exposure. PMID: 27923581
- c-fos induction depends on KCl concentration but Bdnf induction does not in cultured rat cortical neurons. PMID: 28634074
- Our results show that there are distinct populations of VMH neurons whose Fos expression is suppressed by hypoglycemia, and their numbers correlate with blood glucose. These findings support a clear division of glycemic control functions within the different parts of the VMH. PMID: 27030665
- c-Fos and BDNF play important roles in morphological development and synaptic communication of immature neurons. PMID: 27028464
- Myocardial infarction induced different time-dependent c-Fos expression patterns in the in the paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus and thalamus. PMID: 27601012
- Forced swimming results in reduced DNA methylation at specific 5'-cytosine-phosphate-guanine-3' (CpG)s within c-Fos and Egr-1 gene promoters and untranslated regions in DG neurons. SAM significantly increases DNA methylation at these c-Fos and Egr-1 gene loci and inhibits c-Fos and Egr-1 induction. PMID: 27078100
- Hippocampus, amygdala, and paraventricular nucleus Fos expression was increased by maternal deprivation. Chronic stress reduced Fos in hippocampus, but increased it in the paraventricular nucleus. PMID: 26452320
- This better performance of reversal learning seemed to be related with the specif of pattern of c-Fos expression in brain regions involved in cognitive flexibility. PMID: 26314630
- The aim of the present work was to assess the levels of mRNA encoded by genes c-jun and c-fos and the ratio of expression levels of these genes in various regions of the neonatal rat brain after the administration of dexamethasone PMID: 27239846
- Results showed that the OR-NORMAL group presented a greater exploration of objects than the OR-CONTEXT group. To label the brain regions involved in novel-object recognition under these conditions, authors marked the expression of c-Fos protein. PMID: 26072392
- Results indicate that levels of c-Fos in the CA1 area and perirhinal cortex correlate with effective exploration, d2, on the respective versions of the novelty preference tests, novel place and novel object recognition PMID: 26216073
- Estradiol downregulates the mRNA and protein expression of c-Fos in lateral habenula tissues. PMID: 26082062
- The study presents distribution of Fos-like immunoreactivity, catecholaminergic and serotoninergic neurons activated by the laryngeal chemoreflex in the medulla oblongata. PMID: 26087133
- Up-regulation of c-Fos is associated with pro-apoptotic function on neuronal apoptosis following intracerebral hemorrhage. PMID: 25354492
- Results show that the D1-D2 heteromer can differentially regulate c-fos expression in the brain in a region-dependent manner either through its activation or through tonic inhibition of neuronal activity PMID: 25446350
- The c-fos protein expression and neuropeptide content in the lungs of asthmatic rats are related with asthma attacks. PMID: 25674230
- After diffuse brain injury, brain water content and c-Fos/c-Jun expression change over time PMID: 25031700
- analysis of expression of FOS protein, as an indicator of neural activation, in the mitral and granular cell layers of the main and accessory olfactory bulbs PMID: 24915133
- The food-acquisition task learning is accompanied by c-Fos induction in the barrel cortex neurons in animals that learned previously a conditioned "whisking" task. PMID: 25710066
- Lateral fluid percussion injury leads to enhanced expression of c-fos, BDNF and Bax within 24 h of traumatic brain injury PMID: 24978397
- Unilateral hippocampal stimulation caused bilateral c-FOS overexpression in ipsilateral amygdala, the hippocampus, dentate gyrus, and hilus. In CA1 and CA3 despite bilateral activation, c-FOS hyperexpression prevailed at the stimulated side over time. PMID: 24118230
- there was no significant difference in c-Fos expression in thethe dentate gyrus of the hippocampus and central nucleus of the amygdala between ACTH- and saline-treated rats PMID: 23922220
- Activation of c-fos in chronic inflammatory pain is regulated by Homer 1b/c in the spinal cord. PMID: 24316406
- Data indicate that mild hypothermia increased the expression of c-fos protein in both hippocampus and cerebral cortex, whereas hyperthermia decreased the expression of c-fos protein. PMID: 24939298
- Intracerebroventricular infusion of CGRP does not induce Fos activation in the trigeminovascular system. PMID: 24321404
- A significant increase in c-Fos expression in an arthritic rat model is reduced by treatment with N-(2-hydroxyphenyl) acetamide. PMID: 24186846
- c-Fos expressionis regulated by nitric oxide in the commissural nucleus tractus solitarii regulates carotid chemoreception hyperglycemic reflex PMID: 24333564
- 5-HT area postrema neurons contribute to an ascending pathway that is linked to the nucleus accumbens, which is a component in the reward network of the brain. PMID: 24598462
- Two distinct patterns of brain activation/c-Fos expression emerge in response to the presence or absence of social stimuli that differ dramatically with the age of the male animals--early adolescence or young adult. PMID: 22851043
- Deep brain stimulation of mediodorsal thalamic nucleus produces robust increases in the expression of zif-268, but not c-fos localised to regions that are reciprocally connected with the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus. PMID: 23660497
- MAPK and PKC pathways had opposing effects on the regulation of c-fos in nucleus pulposus PMID: 24023832
- Data indicate that administration of losartan and more strongly moxonidine modulated most effects and particularly inhibited Fos-activity in locus coeruleus neuron. PMID: 23818940
- The effects of sodium on c-Fos metabolism in the ENaC-expressing neurons of the sensory circumventricular organs are reported. PMID: 24049115
- The aim of this study was to define all the areas of changes in expression of nuclear c-Fos protein (c-Fos), cytoplasmic somatostatin (SS) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) in rat brain during experimental ischemia. PMID: 24308227
- dopamine input may contribute to footshock- induced activation of cFos expression in the lateral habenula. PMID: 23593280
- This study demonistrated that c-FOS was induces expression in brainn during Intracranial self-stimulation. PMID: 23624190
- Extracellular recording and immunochemistry methods were used to analyze the discharge of neurons and c-Fos protein expression in the NTS following acupuncture at different acupoints and a nonacupoint. PMID: 23591003
- Data indicate that c-fos plays an important role in myocardial lesions and is likely to be involved in the pathogenesis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) as well. PMID: 23054911
- The present findings with c-Fos activity mapping method indicated a novel possibility of the differential regulation of ocular dominance plasticity PMID: 23333670
- These findings suggest that though the networks of cells that participate in behavior or seizure-induced activity are largely maintained in aged rats, their RNA transcript levels are altered. PMID: 23158763
- Nociceptive stimulation increased c-fos expression in spinal cord and hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. PMID: 22960202
- Maternal separation did not significantly affect Fos expression in the hippocampus, but environmental enrichment increased Fos expression. PMID: 23195113
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Nucleus. Endoplasmic reticulum. Cytoplasm, cytosol.
-
蛋白家族:BZIP family, Fos subfamily
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
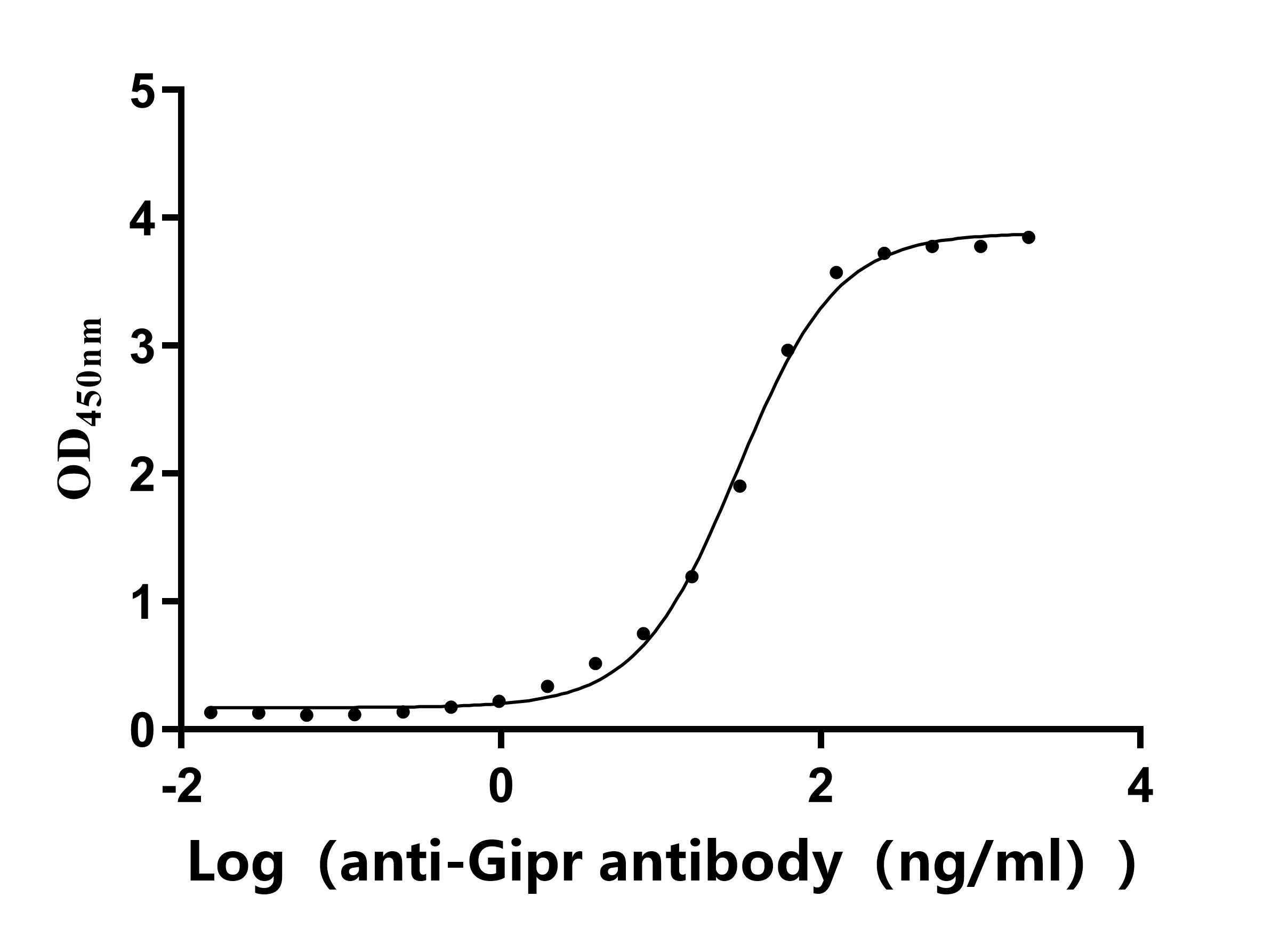
Recombinant Rat Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
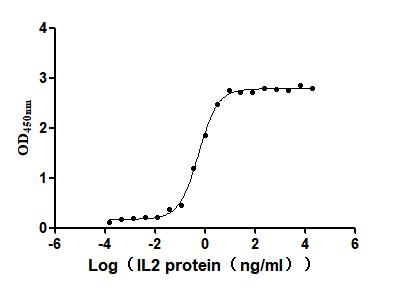
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
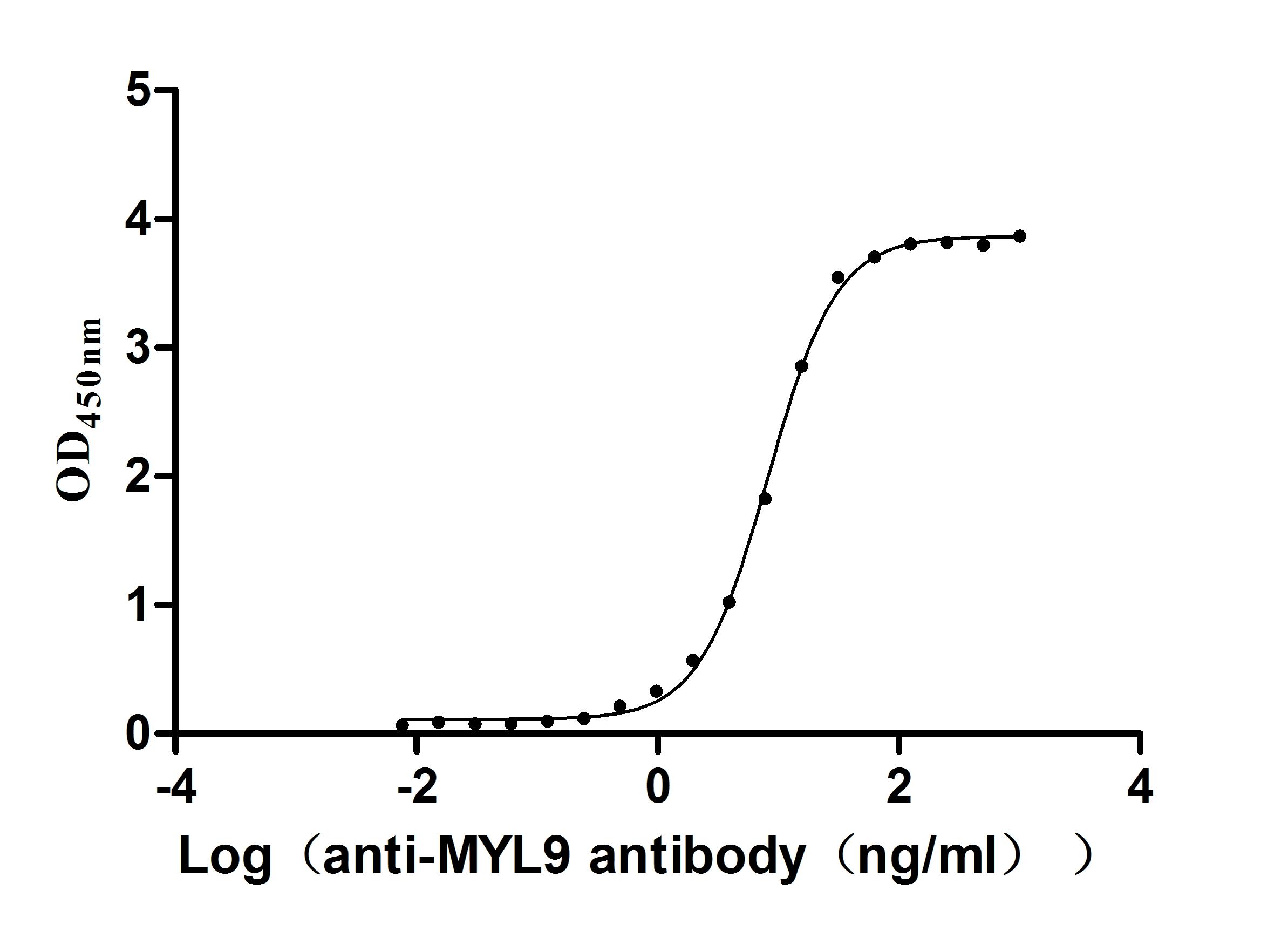
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B (MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
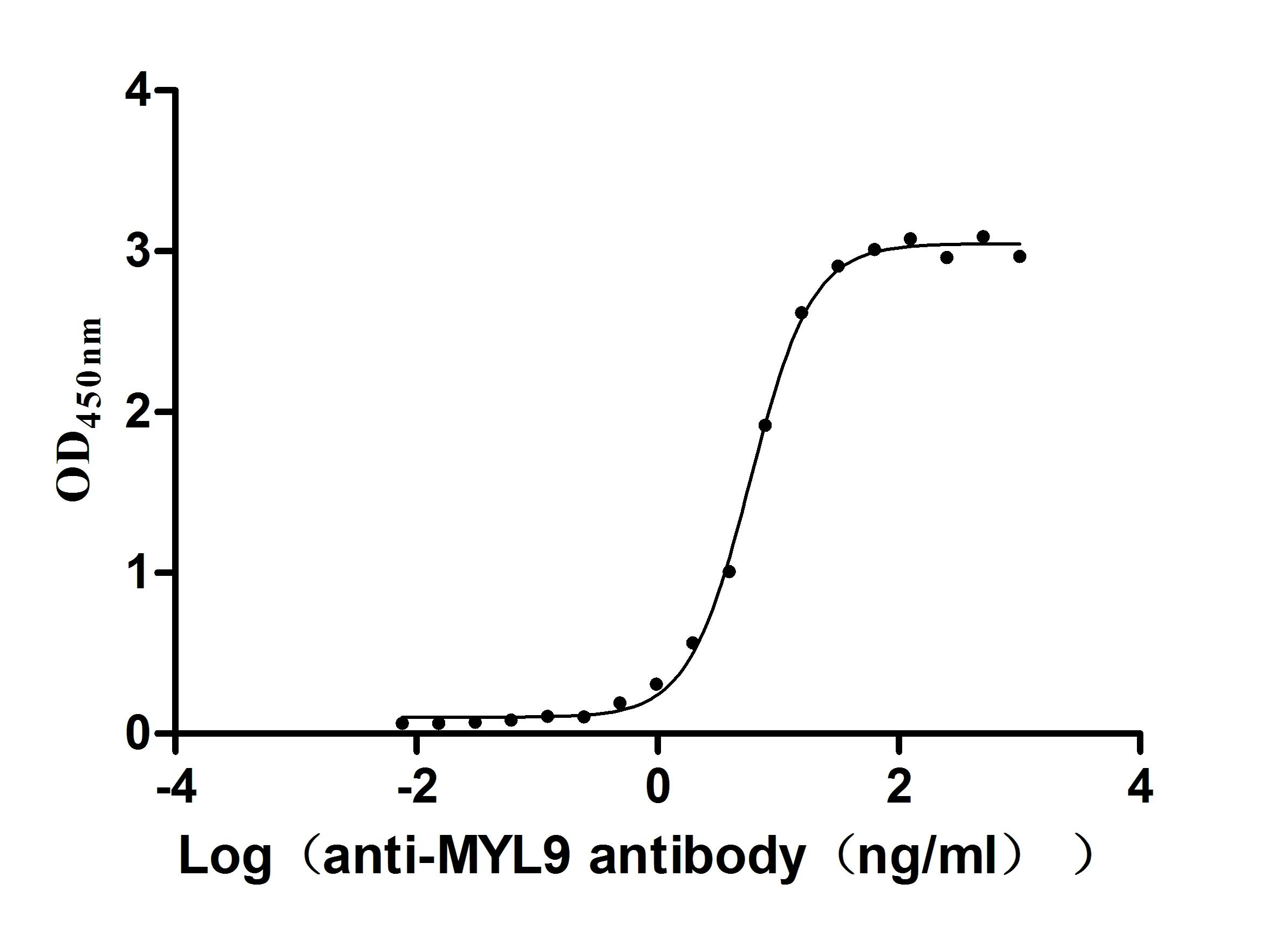
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12A (MYL12A) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)